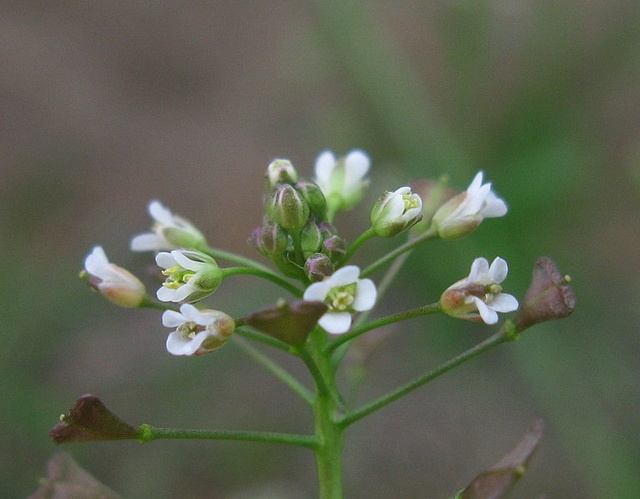
Shepherd’s purse seedling benefits from animal proteins
Shepherd’s purse seeds derive nutrients from small animals by attracting, ensnaring, killing and digesting them, Hattie Roberts and colleagues discovered. The plant is carnivorous during early development.
Most carnivorous plants have a striking appearance: bladderworts, Venus flytrap, pitcher plants and sundews capture small critters with ingenious traps or sticky leaves. But who would suspect shepherd’s purse of having a carnivorous diet? The plant, which occurs almost everywhere, looks innocent. Still, it captures small invertebrates and uses their proteins when germinating, Hattie Roberts and colleagues write. Apparently, also less spectacular carnivores exist among plants.
Animal proteins
 A shepherd’s purse plant (Capsella bursa-pastoris) does not capture any bugs, but the seeds do. In moist soil, they are covered with a tough, sticky mucus layer. Years ago, John Barber already showed that germinating seeds excrete an attractive substance that lure small invertebrates, which subsequently are entrapped and killed by a toxin – Barber used mosquito larvae in his experiments. The seeds also release enzymes that digest animal proteins and take up the building blocks, amino acids.
A shepherd’s purse plant (Capsella bursa-pastoris) does not capture any bugs, but the seeds do. In moist soil, they are covered with a tough, sticky mucus layer. Years ago, John Barber already showed that germinating seeds excrete an attractive substance that lure small invertebrates, which subsequently are entrapped and killed by a toxin – Barber used mosquito larvae in his experiments. The seeds also release enzymes that digest animal proteins and take up the building blocks, amino acids.
The seeds seem to use animal proteins for growth, Barner stated. They also attract and kill nematodes (roundworms that live in soil), unicellular organisms and bacteria.
Food supply
Now, Hattie Roberts completes the story. She germinated seeds in presence or absence of nematodes and monitored germination and growth of the seedlings. The experiments showed that the seeds do better when animal nutrients are available. In soils in which nematodes were present, more seeds germinated successfully than in soils without nematodes, and the seedlings were bigger and heavier when measured ten days after germination. After three weeks, young plants that had germinated in soil with nematodes had longer roots and larger leaves.
Although seeds of shepherd’s purse are able germinate without animal nutrients, they do better with such nutrients. On soils with low nutrient levels, seeds derive more benefits from animal nutrients than on soils with high nutrient levels, as shown by the experiments.
Shepherd’s purse seeds are small and contain only a minimal food supply for the seedling. That is why the plants profit from extra nutrients during early development.
Willy van Strien
Photos:
Large: shepherd’s purse flowers. Harry Rose (Wikimedia Commons, Creative Commons CC BY 2.0)
Small: shepherd’s purse seeds. Kinori (Wikimedia Commons, public domain)
See also:
Carnivorous plants with spectacular traps: bladderwort and Venus flytrap
Sources:
Roberts, H.R., J.M. Warren & J. Provan, 2018. Evidence for facultative protocarnivory in Capsella bursa-pastoris seeds. Scientific Reports 8: 1012. Doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28564-x
Barber, J.T., 1978. Capsella bursa-pastoris seeds. Are they “carnivorous”? Carnivorous Plant Newsletter 7: 39-42.